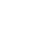

Wet Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD) is used for coal-fired power plants to remove SO2 from flue gas emissions.
Because coal is rich in a variety of heavy metal elements. these elements undergo a series of chemical reactions at high temperatures in the furnace. resulting in a variety of different compounds. some with the slag out of the furnace. and the other with the flue gas into the desulfurization tower. The limestone slurry is absorbed in the slurry.
The impurities contained in the desulfurization wastewater are mainly suspended solids. supersaturated sulfites. sulfates and heavy metals.
Since the water quality of the desulfurization wastewater is different from other industrial wastewaters. it is difficult to handle. Therefore. the desulfurization wastewater must be treated separately.
FGD blowdown wastewaters has very high levels of chlorides (4.000 – 20.000 mg/L). trace concentrations of heavy metal e.g. chromium. mercury. and selenium. often high levels of nitrates (10–700 mg/L). and very high levels of total dissolved solids (20.000 to 60.000 mg/L).
|
parameter |
unit |
Influent water quality |
| TSS | mg/l | 250-20000 |
| TDS | mg/l | 15000-35000 |
| PH | - | 4-6 |
| Cl﹣ | mg/l | 10000-25000 |
| COD | mg/l | 200-500 |
| NH4﹢ | mg/l | 20-60 |
| NO3﹣ | mg/l | 30-120 |
| Ca²﹢ | mg/l | 300-5000 |
| Mg²﹢ | mg/l | 50-4000 |
| SO4²﹣ | mg/l | 3000-5000 |
| F- | mg/l | 40-100 |
| Al | mg/l | 20-200 |
| As | mg/l | 0.5-0.8 |
| B | mg/l | 1-10 |
| Cd | mg/l | 0.05-0.1 |
| Cr | mg/l | 0.3-1 |
| Fe | mg/l | 80-400 |
| Se | mg/l | 1-4 |
| SiO2 | mg/l | 50-300 |